AASL Column, November 2018
Lucy Campbell and Barbara Opar, column editors
Worth the risk?
Column by Lucy Campbell, Librarian, NewSchool of Architecture and Design
Information professionals concur that fundamentally, libraries are about information access. This concept encompasses all the ‘abilities’ we love to talk about: findability; retrievability; browseability, usability, discoverability and of course availability. For architecture and design librarians, this creates a conundrum. The desire to make information available conflicts directly with the desire to maintain collections. But with increased access comes increased risk. Architecture and design books are generally more expensive than those in other subject areas. They are often not designed for libraries in terms of their format and binding. One must also consider the inherent value of the object versus the intellectual content. Architecture is a discipline in which recent titles can quickly become out of print, and/or prohibitively expensive. An item that cost less than $30 can, within a few short years, be worth much, much more. To be fair, not every book increases in value. The size of the print run, timeliness of the topic, and interest in the author’s writings all come into play when determining value. A recently out of print may have a higher replacement cost than one from some time ago.
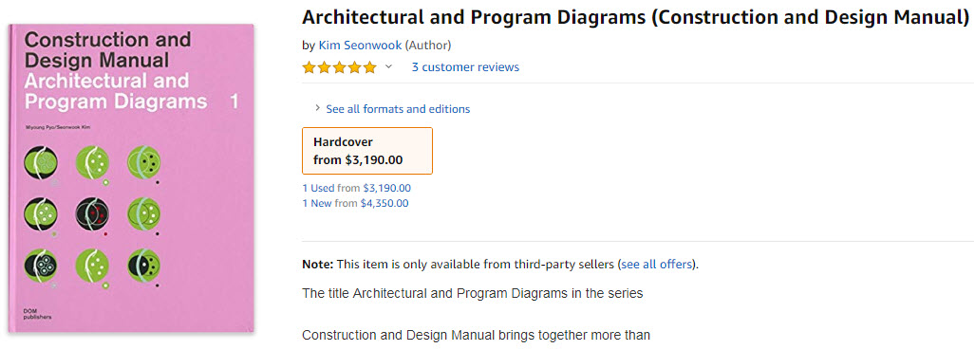
For example, Bernard Tschumi’s Manhattan Transcripts (1994) could set you back anywhere from $200 to $700. Kengo Kuma’s 2006 contribution to Architecture Words, a series of deceptively small paperbacks, now fetches nearly $2,000. The first volume of the popular Construction and Design Manual series Architectural and Program Diagrams (2012) now sells for anywhere from $2,500 to over $4,000. At NewSchool, such items are shelved in the open stacks and circulate. We operate on the principle that academic libraries exist to increase access to knowledge, not lock it away. However a few months ago a faculty member left a 2014 exhibition catalog in a café, and upon attempting to replace it was horrified to discover in four short years its worth had increased from $65 to $1,000.
So what to do? We could not reasonably expect an employee using resources for class preparation to pay up, especially when he had no prior knowledge of the books value. Simultaneously, budget restrictions prevented us from replacing it. Ultimately, we resigned ourselves to the loss of an irreplaceable item. This painful problem led us to rethink our principles and reach out to other professionals for solutions.
We were surprised to learn the myriad approaches in existence. While the care, handling and storage of rare books is widely discussed, there is currently no generally accepted practice for expensive items in regular use. Our colleagues utilize a variety of approaches, some of which include:
- Relocating expensive items to closed collections (for example library cupboards, cages, or shelves behind circulation desks)
- Creating specific collections with short circulation parameters and prohibitive fines
- Making items non-circulating while keeping them in the open stacks to maintain browseability
- Keeping a running list of high value items
- Adding labels to items identifying them as rare, expensive, or both
- Flagging items with warning messages in library management systems
- Trusting patrons to be responsible
Each approach rouses concerns in the age old debate of steward versus gatekeeper: reducing access can discourage use; labels may make items targets for theft; and watch lists require consistent consultation. While libraries are revisiting access to unique and costly materials, some are still trying to maintain control. Breaking up collections of complete works and allowing them to circulate can make them less accessible and useable. Patrons have difficulty identifying where things are located when changes are made.
When I joined NewSchool the library had a confusing number of collections. Having worked to merge them and increase browseability, it seems counter intuitive to start creating separate collections again. At a time when libraries are constantly required to justify the space they occupy, policies that might reduce circulation statistics and/ or perceived value make little sense. We should be celebrating these unique collections, not hiding them from scholars and students.
Ultimately we chose to flag items worth $200 plus with a stop message and inform patrons at the desk of item value. In the past three months 14 items have been flagged. We make sure to explain our replacement policy, and hope this impresses a stronger sense of responsibility on users.
Our decision was based solely on conversations with colleagues and informal debate, but it would be interesting to draw some evidence-based conclusions about best practices. Such work could inform libraries how best to ensure access and prevent losses. Digitization may in due course be the answer to this problem.
In general libraries – especially larger public institutions- are moving towards increasing access to unique and costly materials. The trend towards access has seen the disbanding of what might be called “medium rare” or limited access collections. As more resources become available in digital format, print collections can be locked up or relocated with justification.
There are many reasons for and against special treatment of unique and costly architecture books. Ultimately it comes down to the mission and objectives of individual libraries. For whom does the collection exist? While librarians must grapple with the ethics of access, faculty should weigh in as well. How important are certain books to your teaching? Your research? Your thoughts and ideas are welcome. Email me at lcampbell@newschoolarch.edu.

 Study Architecture
Study Architecture  ProPEL
ProPEL